PSC HSST Computer Science Model Questions and Answers – Part 3
51. A point to point link that supports data flowing in only one direction at a time
(A) Simplex link (B) Half Duplex link
(C) Full Duplex link (D) Leased Line
Answer: B
52. A networking device used to connect similar types of LANs.
(A) Bridge (B) Repeater
(C) Hub (D) Medem
Answer: A
53. A SIM card contain:
(A) Personal Identification Number
(B) International Mobile Subscriber Identity
(C) Authentication key
(D) All of these
Answer: D
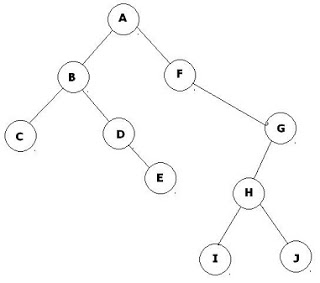
54. In the given tree, in what order does the vertices are processed if in-order traversal is used:
(A) ABCDEFGHIJ (B) CBDEAFIHJG
(C) CEDBIJHGFA (D) CBEDAFGIHJ
Answer: B
55. IC 74 LS 138 is a:
(A) NOR gate (B) Decoder
(C) Latch (D) Tri-state Buffer
Answer: B
56. Binary search algorithm employs the strategy of.
(A) Divide and Conquer technique
(B) Dynamic Programming
(C) Branch & Bound technique
(D) Greedy Strategy
Answer: A
57. Dangling-else ambiguity can be eliminated by.
(A) Matching else with nearest if
(B) Matching else with unmatched if
(C) Removing last occurrence of else
(D) Matching else with nearest unmatched if
Answer: D
58. Among the following, a representation that can be used for designing a system as a collection of procedures or modules:
(A) Data flow diagrams (B) Activity Chart
(C) Flow chart (D) ER Modeling
Answer: A
59. In C++, the following statements causes.
#include<iostream.h>
int main()
{
int x=10,y=5;
int* p=&x;
int* q=&y;
p=q;
delete(p);
return (0);
}
(A) p-a dangling reference
(B) q-a dangling reference
(C) Both p and q as dangling references
(D) None of these
Answer: C
60. Conversion from one data type to another data type, inserted automatically by a programming language.
(A) Polymorphism (B) Coercion
(C) Auto Binding (D) Dynamic Binding
Answer: B
61. The process of testing individual components in a software.
(A) Interface Testing (B) Partition Testing
(C) Unit Testing (D) Structural Testing
Answer: C
62. In C++, the operator which cannot be overloaded.
(A) Bitwise & operator (B) Assignment operator
(C) == operator (D) :: operator
Answer: D
63. A solution to external fragmentation.
(A) Segmentation (B) Compaction
(C) Swapping (D) Thrashing
Answer: B
64. A type of inheritance in which the property of one class is inherited by more than one class.
(A) Hybrid Inheritance (B) Hierarchical Inheritance
(C) Multilevel Inheritance (D) Multiple Inheritance
Answer: B
65. The worst case time complexity of merge sort algorithm for input size n.
(A) q(n) (B) q(n2)
(C) q(log n) (D) q(nlog n)
Answer: D
66. A full adder circuit with x, y and z as input bits produces an output, the binary sum represented by.
(A) x+y+z (B) xÅyÅz
(C) xyÅxzÅyz (D) xy+xz+yz
Answer: B
67. If a variable is declared as register type, then the operator that cannot be applied to it.
(A) Unary & (B) Unary –
(C) Binary & (D) Binary –
Answer: A
68. If grammar G=(N,å,P,S) with non terminal N={S}, terminals å={0,1} and production rules.
S®0S, S®S1, S®0, then L(G)=
(A) 0*01* (B) 0*1*
(C) 0*11* (D) 0*1*0
Answer: A
69. What would be the output of the following C program.
#include<stdio.h>
main()
{
int x=1;
while(x<=1);
{
printf(“Good Morning”);
--x;
}
}
(A) Good Morning (B) Good Morning infinite times
(C) Blank Display (D) Syntax Error
Answer: C
70. In a compiler, the task of scanning the source code, to recognize and classify various elements is known as.
(A) Code Optimization (B) Syntactic Analysis
(C) Lexical Analysis (D) Semantic Analysis
Answer: C
71. Time complexity of Prim’s minimum spanning tree algorithm is:
(A) q(n) (B) q(log n)
(C) q(nlog n) (D) q(n2)
Answer: D
72. A fact in prolog is a special case of a:
(A) Query (B) Rule
(C) Term (D) Goal
Answer: B
73. Grammars that can be translated to DFAs:
(A) Left linear grammar (B) Right linear grammar
(C) Generic grammar (D) All of these
Answer: B
74. An example of a compiler-compiler is:
(A) JAVA (B) LEX
(C) YACC (D) MATLAB
Answer: C
75. A relation R on a set X is said to be a partial ordering if R is:
(A) Reflexive, Symmetric, Transitive
(B) Reflexive, Symmetric, Non-Transitive
(C) Reflexive, Anti-Symmetric, Transitive
(D) Reflexive, Anti-Symmetric, Non-Transitive
Answer: C